Hello and welcome to exampundit. This was shared with us by our mentor Baahubali. This article covers CTS, CBS and Interest Rates i.e. basic banking functions.
CTS
- CTS stand for Cheque Truncation System.
- Started in 2008.
- This system eliminates the physical movement of cheques and provides a more secure and efficient method for cheque clearing.
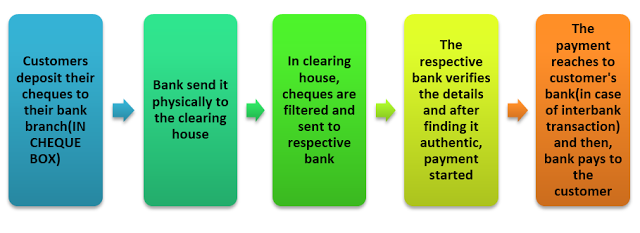
Now, the question arises why CTS came in existence? To answer this we have to understand the traditional method of cheque clearing. It can be explained as
In whole transaction, bank takes at least 1-2 days. To make the whole process fast, CTS came into existence.
Under this system, an electronic image of the cheque is transmitted to the drawee branch by clearing house along with relevant information like MICR band, date of presentation, presenting bank etc.
Merits of CTS:
o Associated cost with the movement of physical cheque gets eliminated.
o Customers have to pay no charge in the clearing process.
o It is efficient for bank and customers both.
Demerits of CTS:
o As cheques are in digital form in CTS, in case of any errors, customers can not correct it. The only solution is – they have to issue fresh cheque.
Interest rates:
In order to expand business, enhance capital, it needs money. We also need money time to time for our different needs. So, we take credit from financial institutions to cater our needs. But these institutions can’t give loan for free. We have to pay some additional amount except principal loan amount. So, the rate at which these financial institutions/banks lend us or give credit facility to us is called interest rates.
Some terminologies related to interest rate
PLR – Prime Lending Rate
o The rate of interest charged by the bank, to their credit worthy customers, is called PLR.
o It is the minimum interest rate.
o RBI has eliminated it in 2010.
Base rate
o The minimum interest rate, decided by commercial bank, below which it cannot lend.
o It is implemented from 2010 in place of PLR.
MCLR – Marginal Cost of funds based Lending Rates
o To provide customers more benefit, RBI started MCLR from 2016.
o In MCLR, RBI linked interest rates with REPO RATE in spite of MARKET CONDITIONS.
Now, the question is – why the concept of MCLR came?
The answer is quite simple –
Whenever RBI cuts the Repo rate, same has to be done by individual banks also in their Base Rates. But they lower the Base Rate in small margin because most banks currently follow average cost of fund based calculations for arriving at respective base rates and due to this only, they lowered Base Rate by 20-40 basis points only where RBI lowered the REPO rate by more than 100 basis points in FY 2015-16.
CBS
o Stands for CORE Banking Solutions
o CORE – Centralised Online Real-time Exchange
o It is the process where branches of a bank are connected to a central host and the customers of connected branches can do banking activity at any branch of corresponding bank with core banking facility.
Advantages of CBS:
For Customers:
o Transaction can be done from any branch.
o Lower incidence of errors
o Better fund management due to immediate availability of funds.
For Banks:
o Better customer service
o Availability of accurate data
o Increase in business volume with better asset-liability management and risk management.
Disadvantages of CBS:
o As whole data is stored in central host, banks have to contact central host everytime in case of any transaction and all. Sometimes we have to suffer from server problems. (Jab bank wala bolta hai – “server down hai..asuwidha k liye khed hai :P”)
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
Regards
Team ExamPundit